-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Definitions
Deterministic algorithm - an algorithm that, given a particular input, will always produce the same output with the underlying machine always passing through the same sequence of states
Complete - refers to the property of being able to simulate everything in the same complexity class
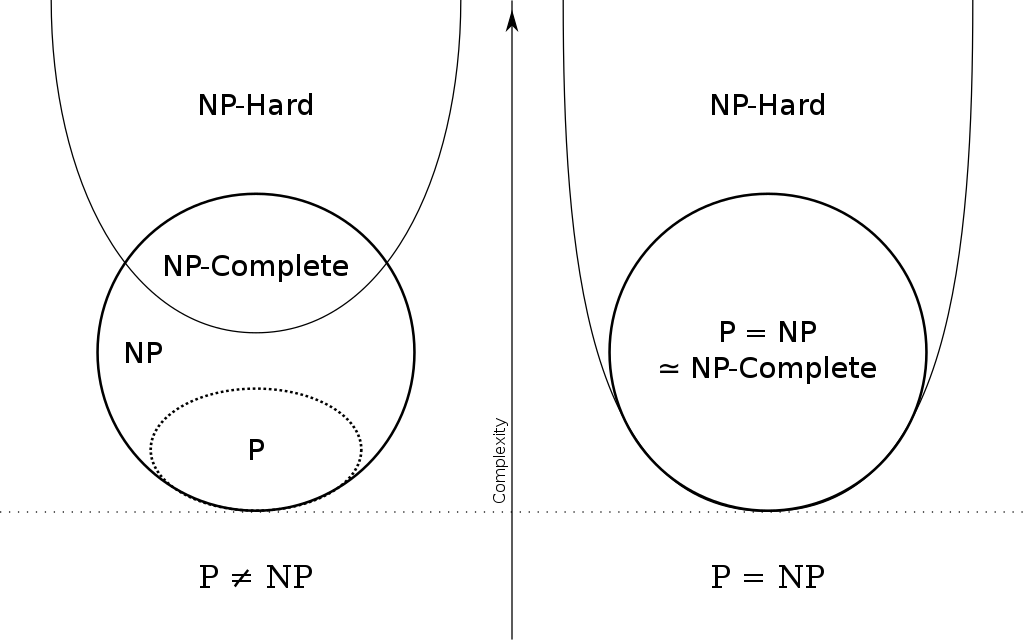
A computational problem x is in the class P if there is a deterministic algorithm that solves x and that runs in polynomial time ..O(n^k) for some k)
- These are polynomial-time problems, often called feasible or tractable, even tho for k > 20 they are not really either.
A computational problem x is in the class NP if there is a non-deterministic algorithm that solves x and that runs in polynomial time ..O(n^k)
- non-deterministic polynomial-time problems, often called infeasible or intractable. These algorithms require some luck to work efficiently. It is easy to verify whether or not a solution is correct
Stands for "non-deterministic polynomial acceptable problems".
It is difficult to find the solutions to these problems.
It is suspected that there are no polynomial-time algorithms for NP-Hard problems, but that has not been proven.
A problem is NP-Complete when:
- It is a problem for which the correctness of each solution can be verified quickly and a brute-force search algorithm can actually find a solution by trying all possible solutions
- The problem can be used to simulate every other problem for which we can verify quickly that a solution is correct. In this sense it is the hardest of the problems to which solutions can be verified quickly so that if we could actually find solutions of some NP-Complete problem quickly we could quickly find the solutions of every other problem to which a solution once given is easy to check.
NP-Complete stands for "nondeterministic polynomial-time complete"
Travelling salesman is NP-Hard.